How Does Thermal Energy Storage Work?
Learn about Thermal Energy Storage (TES), a technology that captures and utilizes heat for later use in power generation and climatic control.
Get Price
The future of wind energy: Efficient energy storage for
These technologies allow wind turbines to be directly coupled with energy storage systems, efficiently storing excess wind power for later use.
Get Price
Energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time [1] to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy
Get Price
Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, is a set of technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later
Get Price
What is energy storage?
Energy storage is the capturing and holding of energy in reserve for later use. Energy storage solutions for electricity generation include pumped
Get Price
Energy Storage for Power Systems | IET Digital Library
Energy storage is an essential part of any physical process, because without storage all events would occur simultaneously; it is an essential enabling
Get Price
Electricity Storage | US EPA
For example, electricity storage can be used to help integrate more renewable energy into the electricity grid. Electricity storage can also help generation facilities operate at
Get Price
Energy storage on the electric grid | Deloitte Insights
Energy storage is critical for mitigating the variability of wind and solar resources and positioning them to serve as baseload generation. In fact, the time is ripe for utilities to go "all in" on
Get Price
What Is Long-Duration Energy Storage? Inside the LDES Market
What is long-duration energy storage? Learn how LDES supports grid reliability, integrates renewables, and powers the clean energy future.
Get Price
What is energy storage?
Energy storage is the capturing and holding of energy in reserve for later use. Energy storage solutions for electricity generation include pumped-hydro storage, batteries,
Get Price
Renewable Energy Generation and Storage Models
Renewable Energy Generation and Storage Models Renewable energy generation and storage models enable researchers to study the impact
Get Price
Renewable Energy Storage Facts | ACP
Energy storage enables us to power the grid using renewables like solar and wind, even when the sun is down or the wind is not blowing. Energy storage
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is
Get Price
What is energy storage power generation used for? | NenPower
Energy storage systems serve as a crucial mechanism for load balancing within power generation and supply networks. This function is pivotal because energy demand
Get Price
Wind power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This
Get Price
Grid energy storage
Electricity can be stored directly for a short time in capacitors, somewhat longer electrochemically in batteries, and much longer chemically (e.g. hydrogen), mechanically (e.g. pumped hydropower) or as heat. The first pumped hydroelectricity was constructed at the end of the 19th century around the Alps in Italy, Austria, and Switzerland. The technique rapidly expanded during the 196
Get Price
Grid energy storage
Energy from fossil or nuclear power plants and renewable sources is stored for use by customers. Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, is a set of technologies
Get Price
Batteries are a fast-growing secondary electricity source for the grid
Instead, they store electricity that has already been created from an electricity generator or the electric power grid, which makes energy storage systems secondary sources
Get Price
Renewable Energy Storage Facts | ACP
Energy storage enables us to power the grid using renewables like solar and wind, even when the sun is down or the wind is not blowing. Energy storage helps smooth out intermittent
Get Price
Energy storage for electricity generation and related processes
Along with the fluctuations of the renewable energy technologies production, storage is important for power and voltage smoothing. Energy storage is also important for energy
Get Price
Why Energy Storage is Just as Important as Generation
By integrating energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, into the grid, we can transform intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar into reliable,
Get Price
What is energy storage power generation used for?
Energy storage systems serve as a crucial mechanism for load balancing within power generation and supply networks. This function is
Get Price
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power
Get Price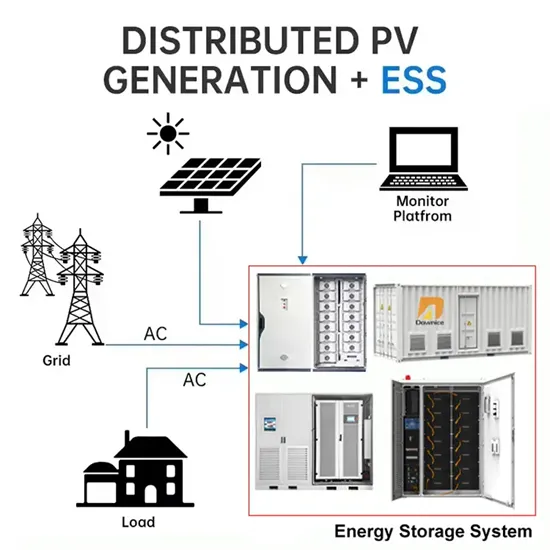
Why Energy Storage is Just as Important as Generation
By integrating energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, into the grid, we can transform intermittent renewable energy sources
Get Price
Systems Development and Integration: Energy Storage and Power Generation
The SDI subprogram''s strategic priorities in energy storage and power generation focus on grid integration of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies, integration with renewable and nuclear
Get Price
Energy Storage – Advanced Power Alliance
Energy storage can be used for various applications, including residential and commercial backup power, transportation, and grid stabilization.
Get Price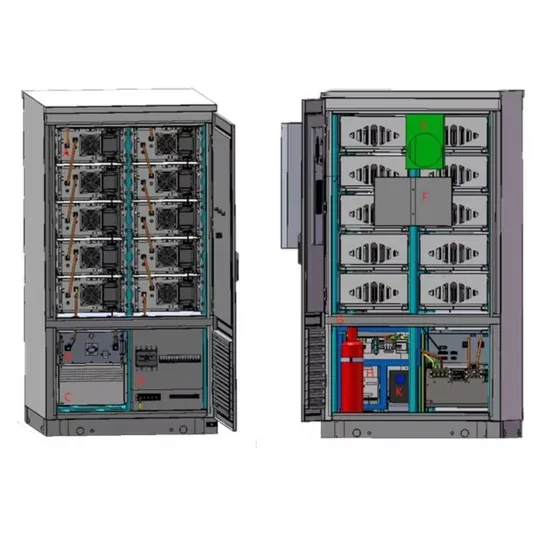
U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet
For example, electricity storage can be used to help integrate more renewable energy into the electricity grid. Electricity storage can also help
Get Price
Battery energy storage system
A rechargeable battery bank used in a data center Lithium iron phosphate battery modules packaged in shipping containers installed at Beech Ridge Energy
Get Price
U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet
Electrical Energy Storage (EES) refers to systems that store electricity in a form that can be converted back into electrical energy when needed. 1 Batteries are one of the most common
Get Price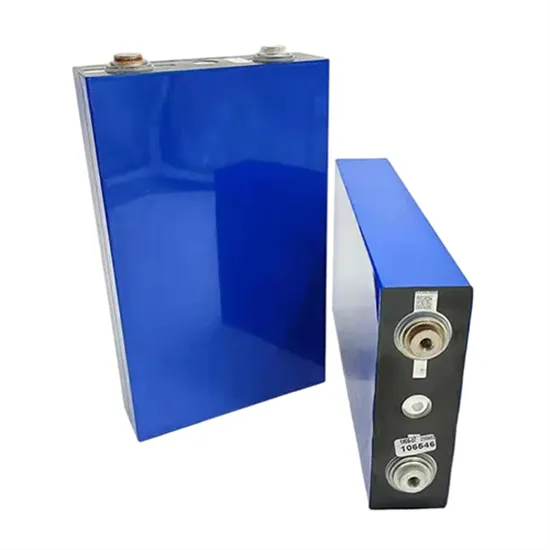
6 FAQs about [Is energy storage used for power generation ]
What is an energy storage system?
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is discharged to supply (generate) electricity when needed at desired levels and quality. ESSs provide a variety of services to support electric power grids.
What are energy storage solutions for electricity generation?
Energy storage solutions for electricity generation include pumped-hydro storage, batteries, flywheels, compressed-air energy storage, hydrogen storage and thermal energy storage components. The ability to store energy can facilitate the integration of clean energy and renewable energy into power grids and real-world, everyday use.
Why do we need energy storage?
Supports the integration of more wind and solar generation: Wind and solar are the cheapest sources of electricity. Energy storage supports the integration of higher and higher shares of renewables, enabling the expansion and incorporation of the most cost-effective sources of electricity generation.
How is energy stored?
Mechanical Energy Storage: Energy is stored through mechanical means, such as compressing air or using flywheels. Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) and flywheels are examples of this technology. Hydrogen Storage: Surplus electricity is used to produce hydrogen through electrolysis.
Why is electricity storage important?
Depending on the extent to which it is deployed, electricity storage could help the utility grid operate more efficiently, reduce the likelihood of brownouts during peak demand, and allow for more renewable resources to be built and used. Energy can be stored in a variety of ways, including: Pumped hydroelectric.
What are the different types of energy storage systems?
Batteries. Similar to common rechargeable batteries, very large batteries can store electricity until it is needed. These systems can use lithium ion, lead acid, lithium iron or other battery technologies. Thermal energy storage. Electricity can be used to produce thermal energy, which can be stored until it is needed.
More related information
-
 What energy storage is used for photovoltaic power generation
What energy storage is used for photovoltaic power generation
-
 Is energy storage used for power generation
Is energy storage used for power generation
-
 Photovoltaic power generation should be equipped with energy storage
Photovoltaic power generation should be equipped with energy storage
-
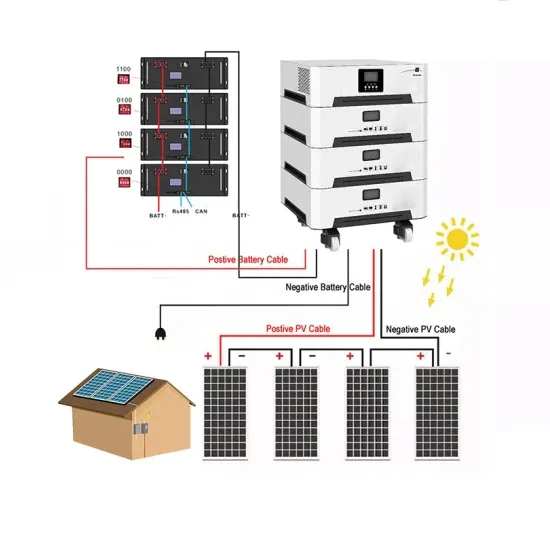 Ethiopian enterprise photovoltaic power generation energy storage cabinet
Ethiopian enterprise photovoltaic power generation energy storage cabinet
-
 Traditional power generation and energy storage
Traditional power generation and energy storage
-
 Is photovoltaic power generation with energy storage in Venezuela
Is photovoltaic power generation with energy storage in Venezuela
-
 Photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in industrial parks
Photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in industrial parks
-
 3kw solar power generation and energy storage
3kw solar power generation and energy storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


