An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize
The base station is a critical component for 5G operation. The base station is comprised of two main components: the active antenna unit (AAU) and the baseband unit (BBU) (see Figure 1).
Get Price
What is 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station is a crucial component of the fifth - generation (5G) mobile network infrastructure. Here''s a more in - depth look at what it is: 1. Definition
Get Price
The Future of Hybrid Inverters in 5G Communication Base Stations
Conclusion: As 5G networks expand, hybrid inverters will play a pivotal role in powering next-gen base stations—providing stable, cost-effective, and green energy solutions
Get Price
5g base station architecture
The backhaul connects the base stations to the core network, while the fronthaul connects the gNB to the DU and CU. Both are critical for ensuring seamless communication
Get Price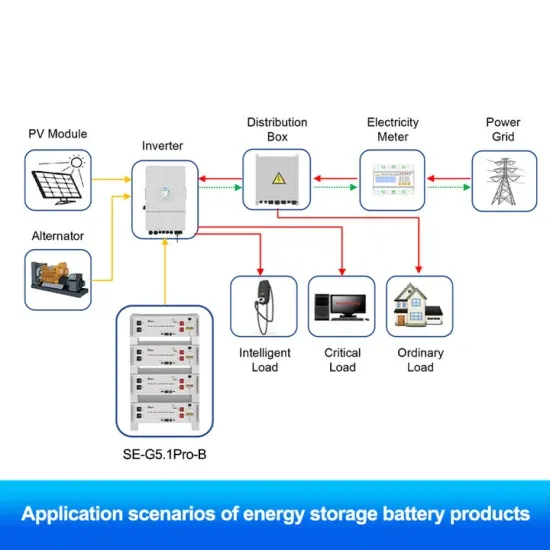
Basic components of a 5G base station
The basic components of a 5G BS, which are illustrated in Figure 1 [20], mainly include communication equipment and power supply equipment. In addition,
Get Price
What is 5G base station architecture?
5G network architecture is a vast improvement upon previous architectures. Huge leaps in performance are made possible by large cell-dense networks. One of the features of
Get Price
Types of Base Stations
Base stations are one of the widely used components in the field of wireless communication and networks. It is an access point or base point of a particular area for
Get Price
What Is a gNB in 5G? Next-Gen Base Station Architecture
It represents the base station in a 5G network architecture, facilitating communication between the user equipment (UE) and the core network. Unlike its
Get Price
Basic components of a 5G base station
The basic components of a 5G BS, which are illustrated in Figure 1 [20], mainly include communication equipment and power supply equipment. In addition, power supporting
Get Price
5G RAN Architecture: Nodes And Components
The 5G RAN architecture is composed of multiple nodes and components that work together to provide seamless connectivity to users. These nodes include the User
Get Price
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture — 5G Mobile Networks: A Systems
The first is to connect new 5G base stations to existing 4G-based EPCs, and then incrementally evolve the Mobile Core by refactoring the components and adding NG-Core capabilities over
Get Price
What Is 5G Base Station?
Base stations, also called public mobile communication base stations, are interface devices for mobile devices to access the Internet. They
Get Price
5g infrastructure
The 5G infrastructure is a complex system that includes various components working together to provide high-speed, low-latency wireless communication. Below is a
Get Price
Quick guide: components for 5G base stations and antennas
Your 5G base-station design and 5G antenna components will need to address not only technical challenges, but also aesthetics, weather and security requirements. This guide
Get Price
COMONENTS OR 5G BASE STATIONS AND ANTENNAS
se-station connects other wireless devices base-station architecture includes various equipment, such as a amplifier, which converts signals from RF antenn.
Get Price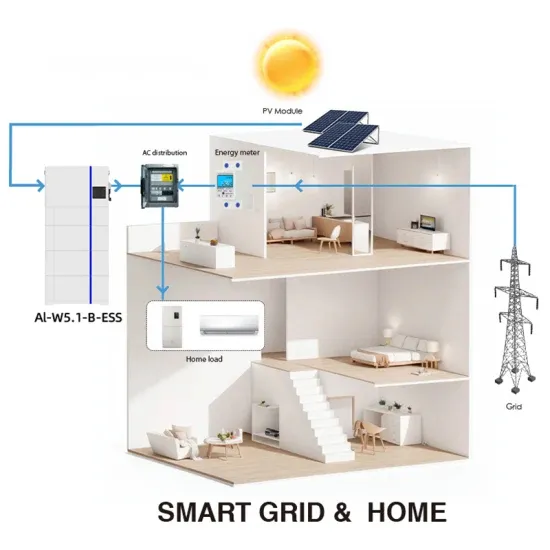
introduction-5g-hardware-components
Explore the essential hardware components powering 5G networks, including RAN elements, Massive MIMO, and edge computing, and their roles in next-gen connectivity.
Get Price
5g gnb architecture
The 5G New Radio (NR) architecture includes the gNB (gNodeB), which is the base station in the 5G network. The gNB plays a crucial role in
Get Price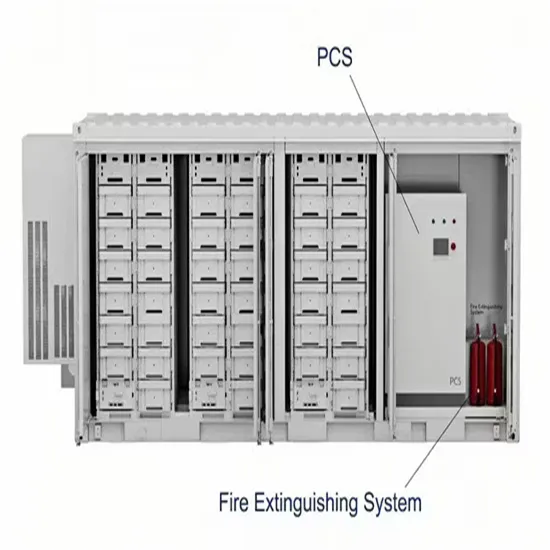
Solutions for Base Station Components | Syensqo
Innovation for Next-Gen Base Stations Base stations are critical in communication for wireless mobile devices, as they serve as a central point in connecting devices to other networks or
Get Price
Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
With the rapid development of 5G communication technology, global telecom operators are actively advancing 5G network construction. As a core component supporting
Get Price
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture — 5G Mobile Networks:
The first is to connect new 5G base stations to existing 4G-based EPCs, and then incrementally evolve the Mobile Core by refactoring the components and
Get Price
5g hardware
Base stations, also known as gNodeBs (gNBs) in 5G, are critical elements in the network infrastructure. They contain antennas and radio frequency (RF) equipment to transmit
Get Price
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless
Get Price
What Are the Key Components of 5G Network
Configured in a distributed and flexible manner, the system includes base stations, antennas, and backhaul connections. Collectively,
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get Price
5G Base Station
5G base station is the core equipment of 5G network, which provides wireless coverage and realizes wireless signal transmission between
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless
Get Price
What Are the Key Components of 5G Network Infrastructure?
Configured in a distributed and flexible manner, the system includes base stations, antennas, and backhaul connections. Collectively, these components provide incredibly high
Get Price
Simplifying Your 5G Base Transceiver Station Transmitter
With wireless communication standards such as LTE and 5G, the emphasis on higher data rates and spectral eficiency has driven the wireless original equip-ment manufacturers (OEMs) to
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The components of the 5G communication base station inverter include]
What are the components of a 5G base station?
Key Components of A 5G Base Station: Antennas and Radios: The Base Station Includes Antennas and Radio Units Responsible for Transmitting and Receiving Signals. Multiple antennas may be used for MOMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), Enhancing Coverage, Capacity, and Overall Network Efficiency.
What are 5G hardware components?
Here's a technical overview of key 5G hardware components: Base stations, also known as gNodeBs (gNBs) in 5G, are critical elements in the network infrastructure. They contain antennas and radio frequency (RF) equipment to transmit and receive signals to and from user devices.
What is 5G base station architecture?
5G base station architecture is characterized by its flexibility, virtualization, and the ability to support diverse services through network slicing. The separation of CU and DU, along with the introduction of cloud-based technologies, allows for more efficient resource utilization and scalability.
What are 5G ran components?
The 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) components are key elements that enable high-speed, low-latency wireless communication. These components include the Radio Frequency (RF) Front End, the Digital Signal Processor (DSP), and the Antenna System. 5G RAN Components Lists: 1. Distributed Unit (DU)
What is 5G ran architecture?
One of the key components of 5G is the Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture, which is responsible for managing the wireless connections between devices and the network. This article will provide a technical overview of the 5G RAN architecture, including its various nodes and components.
What are 5G ran nodes?
These nodes include the User Equipment (UE), the Base Station (BS), the Central Unit (CU), and the Distributed Unit (DU). The 5G RAN architecture also includes several key components, including the Radio Frequency (RF) Front End, the Digital Signal Processor (DSP), and the Antenna System.
More related information
-
 Iraq 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected energy storage
Iraq 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected energy storage
-
 What does a photovoltaic communication base station inverter include
What does a photovoltaic communication base station inverter include
-
 Yaounde 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected project
Yaounde 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected project
-
 What does the Finnish communication base station inverter include
What does the Finnish communication base station inverter include
-
 Communication 5G base station types include
Communication 5G base station types include
-
 Liberia 5G communication base station inverter project
Liberia 5G communication base station inverter project
-
 Moldova 5G communication base station inverter grid connection
Moldova 5G communication base station inverter grid connection
-
 5G communication base station inverter energy storage
5G communication base station inverter energy storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


