Coal fired power plant
Figure 1. A coal fired power plant in England. [1] Note the two tall smoke stacks where the combustion products go into the atmosphere and the shorter, wider
Get Price
How much energy will new semiconductor factories
New semiconductor factories in the US could each use as much electricity as a town — will they run on renewable energy? A new report
Get Price
How Much Electricity Does a Small Factory Use? A Comparative
This article aims to shed light on the power requirements of small factories, warehouses, and businesses, with a particular focus on the contexts of the United Kingdom and the United States.
Get Price
Power station Facts for Kids
A power station (also called a power plant) is a special place where electricity is made. Most power stations have big machines called generators. These
Get Price
How does a nuclear power plant generate electricity?
Nuclear power is one of the ways humans produce electricity. The term nuclear power refers to the source of this energy--the nucleus of atoms! Here''s how it works. Inside a nuclear power
Get Price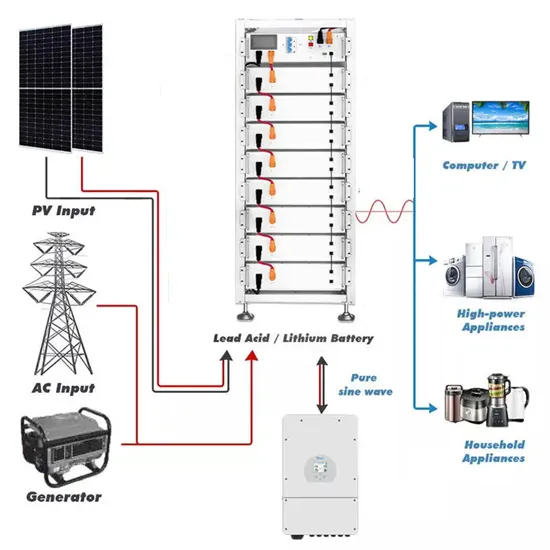
Electricity explained Electricity generation, capacity, and sales in
Energy storage systems for electricity generation have negative-net generation because they use more energy to charge the storage system than the storage system
Get Price
Power Station
The Power Station is a large player built facility that produces power. It does not require power to function and can be upgraded to add more production options.
Get Price
What are the factory energy storage power stations?
There are various technologies employed in factory energy storage power stations, each with distinct advantages and intended applications. The
Get Price
Huntly Power Station
The Huntly Power Station is the largest thermal power station in New Zealand and is located in the town of Huntly in the Waikato. It is operated by Genesis
Get Price
Power
Most buildings require electricity, or power, to function. Power is produced in power generators (see below), stored or discharged from Power Storages,
Get Price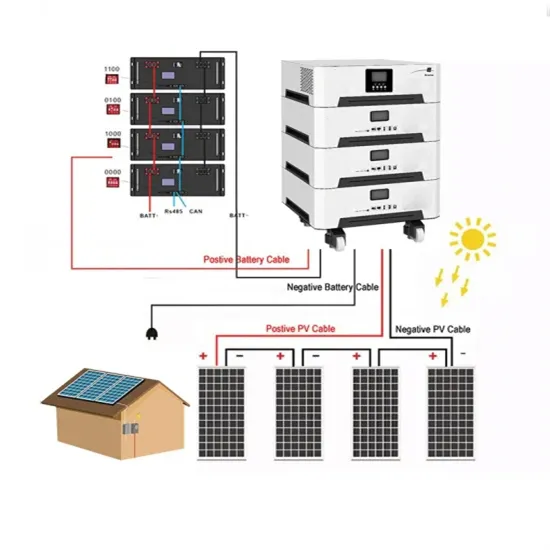
Delivery to consumers
The electric power grid Electricity is generated at power plants and moves through a complex system, sometimes called the grid. The grid includes electricity substations,
Get Price
Electricity for Manufacturing
How Much Electricity Does a Manufacturing Company Use? Manufacturing facilities use 95.1 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity and
Get Price
Business Energy Advisor | Manufacturing Facilities
Process heating, drivepower, cogeneration, and boiler use generally consume the most energy in manufacturing facilities regardless of
Get Price
Industrial power plants
Make an investment in your independence – and ensure a reliable and flexible power supply for your processes. Electricity and heating are major cost factors for industrial plants. That means
Get Price
What are the factory energy storage power stations? | NenPower
There are various technologies employed in factory energy storage power stations, each with distinct advantages and intended applications. The most prevalent method involves
Get Price
How Does a Coal Power Plant Work?
Thermal-based power plants can produce electricity from coal or other fuel sources. The coal-fired process requires three different steps to turn energy released from burning coal to generating
Get Price
How Generators in Power Stations Work
Hydroelectric power stations use the kinetic energy of falling water to generate electrical energy. Some hydroelectric power stations use water
Get Price
Business Energy Advisor | Manufacturing Facilities
Process heating, drivepower, cogeneration, and boiler use generally consume the most energy in manufacturing facilities regardless of subsector. As a whole, manufacturing
Get Price
Power Plant Generators: What It Is? How Does It Work?
In this guide, we''ll walk you through the role of power plant generators, their importance, and how a generator functions as a secondary source of electric energy in various
Get Price
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How much electricity does a power plant generate? The amount of electricity that a power plant generates depends on its electricity generation capacity and on the amount of time the
Get Price
Power Plant Basics: Types, Components, and How
In its simplest form, a Power Plant, known also as a Power Station, is an industrial facility used to generate electricity. To generate power, an
Get Price
How much power do large industrial facilities use? Have any of
Each ASML EUV tool uses about 1 MW of electricity. A typical super fab will have 10 of them. That''s 10 MW for just one process in a set of hundreds. I wouldn''t be surprised if the big
Get Price
Electricity in factories
Electric Power Distribution in a Factory mainly operates on higher voltage ranges than the normal operating ranges in households. High voltages like 11KV, 33KV, 66KV, or 132KV from the
Get Price
Power Plant Guide: Type, Function, and Steam Process
Learn about power plant types, core functions, and how the steam process drives electricity generation in modern energy systems.
Get Price
What type of energy does a factory use?
Industry and manufacturing rely heavily on natural gas (30% of all energy consumed by the industrial sector in 2015), petroleum and other liquids (26%), and electricity
Get Price
How much power do large industrial facilities use? Have any of
Each ASML EUV tool uses about 1 MW of electricity. A typical super fab will have 10 of them. That''s 10 MW for just one process in a set of hundreds. I wouldn''t be surprised if
Get Price
Electricity for Manufacturing
How Much Electricity Does a Manufacturing Company Use? Manufacturing facilities use 95.1 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity and 536,500 Btu of natural gas per square
Get Price
Power Plant Generators: What It Is? How Does It Work?
In this guide, we''ll walk you through the role of power plant generators, their importance, and how a generator functions as a secondary
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What electricity does the factory power station use ]
How do electric power stations work?
Electric power stations use diesel-fueled generators for an internal combustion process that converts diesel’s chemical energy into thermal energy to produce a mechanical action that generates electric power. Mostly diesel plants are used as supplementary or emergency sources of power rather than primary power sources.
What is a power plant & how does it work?
In its simplest form, a Power Plant, known also as a Power Station, is an industrial facility used to generate electricity. To generate power, an electrical power plant needs to have an energy source. One source of energy is from the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas. These fuels are burned in boilers to produce steam.
What is a power plant?
Gigantic energy factories, known as “Power Plants,” are industrial facilities that generate electricity on a large scale. Power stations, also referred to as generating plants, are usually attached to an electrical grid. They contain one or more generators and a rotating device that converts mechanical energy into electric energy.
What energy sources do power plants use?
The majority of power plants use fossil fuels like oil, natural gas, or coal to produce electric power. Other energy sources include hydropower, nuclear power, etc. The type of main energy source defines the power plant type. The uses of diesel backup generators differ based on the type of power plant. Let’s learn about them in detail. 1.
What type of energy does a factory use?
Industry and manufacturing rely heavily on natural gas (30% of all energy consumed by the industrial sector in 2015), petroleum and other liquids (26%), and electricity (10%), with coal, renewables, and biofuels making up the rest. How do factories get their power?
How does a power plant make electricity?
A power plant is a big system that makes electricity. It takes energy from fuel (like gas, coal, or wind) and turns it into electrical power that we use in factories, homes, and everywhere.
More related information
-
 What is the best way to generate electricity for Tajikistan s power station
What is the best way to generate electricity for Tajikistan s power station
-
 What size inverter should I use for a 57kw power station
What size inverter should I use for a 57kw power station
-
 What power supply does Huawei s 5G base station use
What power supply does Huawei s 5G base station use
-
 What is the price of electricity generated by the power station
What is the price of electricity generated by the power station
-
 What is the manufacturer of power station energy storage equipment
What is the manufacturer of power station energy storage equipment
-
 What is the energy storage power station project in Mongolia
What is the energy storage power station project in Mongolia
-
 Which platform should I use for Bulgarian Communications BESS power station
Which platform should I use for Bulgarian Communications BESS power station
-
 What is the total investment in the Liberian energy storage power station
What is the total investment in the Liberian energy storage power station
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


