base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. It plays a central role in enabling
Get Price
5g Base Station Market Size & Share Analysis
The 5G base station is a fixed communication equipment that connects using a single or several antennas. It includes a wireless receiver
Get Price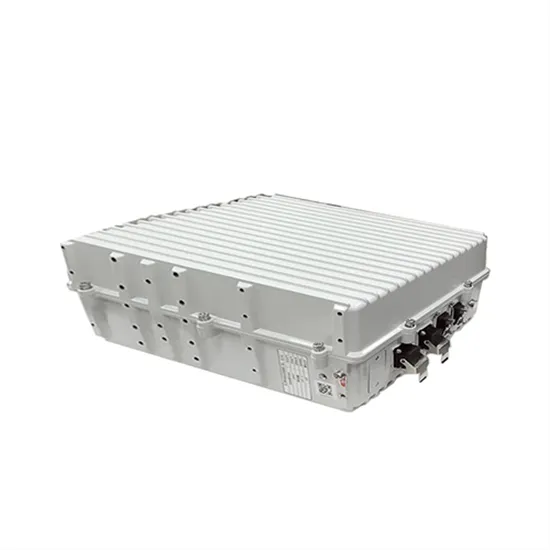
5G RAN Architecture: Nodes And Components
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network that connects devices, such as smartphones and IoT (Internet of Things) gadgets, to the core network and
Get Price
Carbon emissions and mitigation potentials of 5G base station in
The emergence of fifth-generation (5G) telecommunication would change modern lives, however, 5G network requires a large number of base stations, whic
Get Price
Quick guide: components for 5G base stations and antennas
Base stations A 5G network base-station connects other wireless devices to a central hub. A look at 5G base-station architecture includes various equipment, such as a 5G
Get Price
base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. It plays a central role in enabling wireless communication between user
Get Price
What is 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station, also known as a 5G NodeB (gNB) in the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) standards, is a radio access point that connects user equipment (such as 5G -
Get Price
What Is A 5G Base Station?
The 5G base station is the core equipment of the 5G network, providing wireless coverage and realizing wireless signal transmission between the wired communication network and the
Get Price
Energy-efficiency schemes for base stations in 5G heterogeneous
In today''s 5G era, the energy efficiency (EE) of cellular base stations is crucial for sustainable communication. Recognizing this, Mobile Network Operators are actively prioritizing EE for
Get Price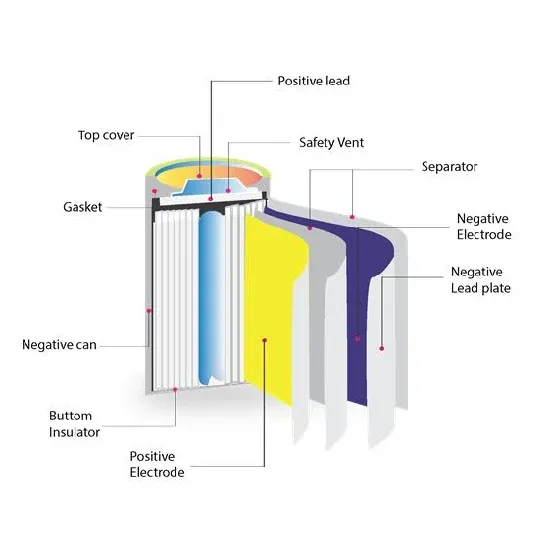
What Is 5G Base Station?
Base stations, also called public mobile communication base stations, are interface devices for mobile devices to access the Internet. They are also a form of radio stations, which
Get Price
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get Price
Integrated control strategy for 5G base station frequency
This paper proposes a double-layer clustering method for 5G base stations and an integrated centralized-decentralized control strategy for their participation in frequency
Get Price
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base stations different?
Base station is a stationary trans-receiver that serves as the primary hub for connectivity of wireless device communication. The architecture of the 5G network must
Get Price
What is the difference between Node B, eNodeB, and gNB?
Node B is the radio base station in 3G UMTS networks; eNodeB is the radio base station in 4G LTE networks; gNodeB (gNB) is the radio base station in 5G NR networks.
Get Price
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get Price
Machine Learning and Analytical Power Consumption
Abstract—The energy consumption of the fifth generation (5G) of mobile networks is one of the major concerns of the telecom industry. However, there is not currently an accurate and
Get Price
What is 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station, also known as a 5G NodeB (gNB) in the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) standards, is a radio access point that
Get Price
What Is A 5G Base Station?
The 5G base station is the core equipment of the 5G network, providing wireless coverage and realizing wireless signal transmission between the wired
Get Price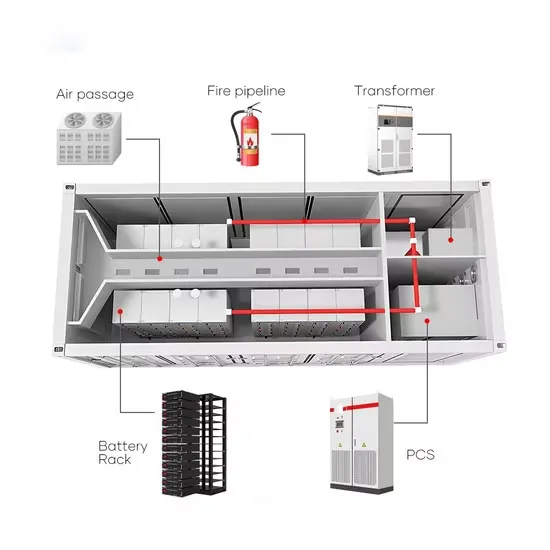
5G base stations and the challenge of thermal management
The 5G base station is a wireless receiver and short-range transceiver that connects wireless devices to a central hub. Its antenna and analog-to-digital converters
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get Price
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base
Base station is a stationary trans-receiver that serves as the primary hub for connectivity of wireless device communication. The
Get Price
5G
SummaryOverviewPerformanceStandardsDeployment5G devicesTechnologyConcerns
5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell communicate by radio waves with a cellular base station via fixed antennas, over frequencies assigned by the base station. The base stations, termed nodes, are connected to switching centers in the telephone network and routers for Internet access by high-bandwidth optical fiber or wireless backhaul connections. As in other cellular networks
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network that connects devices, such as smartphones and IoT (Internet of Things) gadgets,
Get Price
An introduction to 5G New Radio architecture
Base stations are the core of the 5G network and critical for the implementation of 5G NR architectures. Source: Nokia Mobile communication
Get Price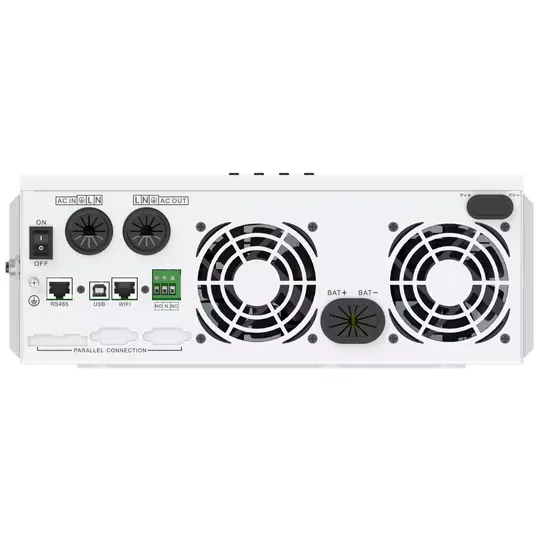
A Secure Transmission Strategy for Smart Grid Communications
As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in smart grids grows, security issues arise, including eavesdropping. The fifth generation (5G) wireless technologies are the driving force
Get Price
5G RAN Architecture: Nodes And Components
Base Station (BS) is a key component of the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture that serves as an access point for wireless connections between user equipment
Get Price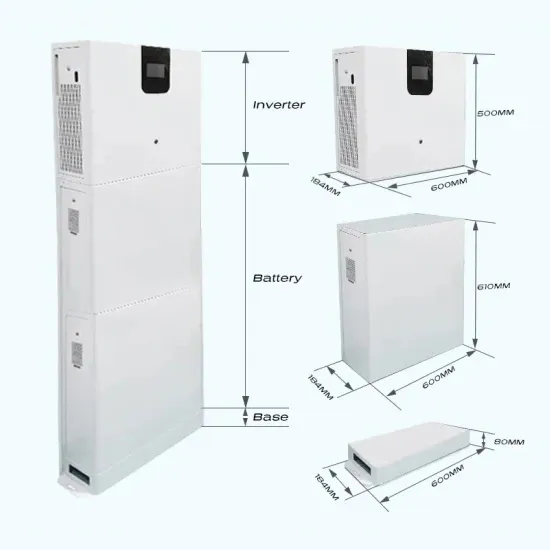
Low-Carbon Sustainable Development of 5G Base Stations in China
Goncalves et al. (2020) explored carbon neutrality evaluation of 5G base stations from the perspective of network structure and carbon sequestration. Despite the growing
Get Price
5G
All 5G wireless devices in a cell communicate by radio waves with a cellular base station via fixed antennas, over frequencies assigned by the base station. The base stations, termed nodes,
Get Price
Optimal configuration of 5G base station energy storage
The high-energy consumption and high construction density of 5G base stations have greatly increased the demand for backup energy storage batteries. To maximize overall
Get Price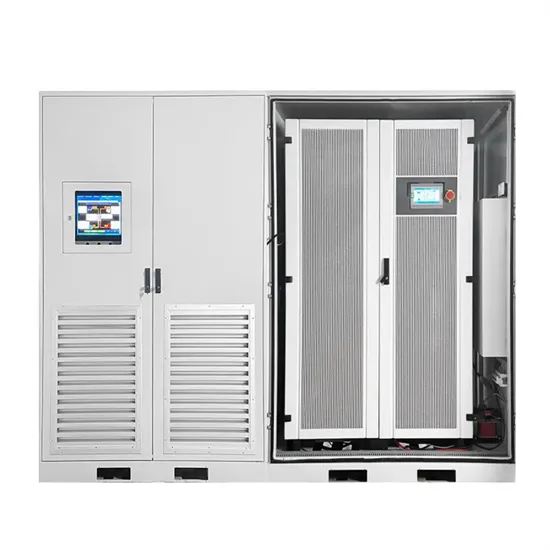
Investigating the Sustainability of the 5G Base Station
5G is the next generation of wireless communication tech-nology that will significantly improve network bandwidth and decrease latency. There are two key wireless communication
Get Price
Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
A 5G base station is the heart of the fifth-generation mobile network, enabling far higher speeds and lower latency, as well as new levels of connectivity. Referred to as gNodeB, 5G base
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Which is the 5G base station for communication ]
What is a 5G network?
5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell communicate by radio waves with a cellular base station via fixed antennas, over frequencies assigned by the base station.
What is a 5G base station?
As the world continues its transition into the era of 5G, the demand for faster and more reliable wireless communication is skyrocketing. Central to this transformation are 5G base stations, the backbone of the next-generation network. These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises.
What are the different types of 5G NR base stations?
This article describes the different classes or types of 5G NR Base Stations (BS), including BS Type 1-C, BS Type 1-H, BS Type 1-O, and BS Type 2-O. 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB.
How does the architecture of a base station affect 5G?
The architecture and shape of the base station directly affect how the 5G network is deployed. In the technical standards, the frequency band of 5G is much higher than that of 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
What is a 5G baseband unit?
The 5G baseband unit is responsible for NR baseband protocol processing, including the entire user plane (UP) and control plane (CP) protocol processing functions, and provides a backhaul interface (NG interface) with the core network and an interconnection interface (Xn interface) between base stations ).
Where is Verizon 5G base station located?
Verizon 5G base station utilizing Ericsson equipment in Springfield, Missouri, USA. 5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells.
More related information
-
 Which is better El Salvador 5G base station or communication
Which is better El Salvador 5G base station or communication
-
 The solution for traditional base station energy storage cabinets in 5G communication
The solution for traditional base station energy storage cabinets in 5G communication
-
 Moldova 5G communication base station battery
Moldova 5G communication base station battery
-
 Communication and 5G base station co-construction plan
Communication and 5G base station co-construction plan
-
 Nigeria 5g communication green base station equipment cabinet manufacturer
Nigeria 5g communication green base station equipment cabinet manufacturer
-
 5g communication base station inverter equipment bsc introduction
5g communication base station inverter equipment bsc introduction
-
 5g base station power supply and communication power supply
5g base station power supply and communication power supply
-
 5G communication base station energy method
5G communication base station energy method
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


