How Many Watts To Run A House? Average 1.2 Kw
Understanding how many Watts it takes to power a home is an important part of managing your energy consumption. In this article, we will explain how many
Get Price
How Much Electrical Power Does A House Need? A
Watts (W): The unit of power. Think of it as the rate at which energy is used. Kilowatts (kW): 1 kW = 1,000 watts. It''s just a larger unit for when
Get Price
How Much Energy Does a Solar Panel Produce?
2 days ago· One kilowatt-hour equals 1,000 watts used for one hour. For example, a 400-watt solar panel produces 400 watts of power in an hour under perfect sunlight. If it gets 5 hours of
Get Price
How Many Watts to Run a House Efficiently
How many watts do I need to run my whole house? To adequately power your entire house, you would need a wattage capacity that goes beyond the average power
Get Price
How Many Watts Does It Take to Run a House?
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know, from average household wattage to how you can calculate your home''s energy use and plan for solar power.
Get Price
How many watts of household energy storage | NenPower
A detailed understanding of the household''s energy profile can help homeowners choose an appropriate energy storage solution, which can enhance energy independence and
Get Price
3-In-1 Solar Calculators: kWh Needs, Size, Savings,
With the increased efficiency of solar panels in the past years, more and more homeowners can decide to power all of their electric appliances with solar
Get Price
How Many Watts Does It Take To Run Your House?
After conducting a thorough analysis of the key factors that impact household energy consumption, it is possible to estimate the average daily wattage consumed by
Get Price
How to Calculate Backup Power Needs for Your
In summary, this household requires 12.24kWh of backup power to endure a 24-hour power outage. Three units of Hinen''s Max 5b 5kWh battery,
Get Price
How to calculate your home battery needs for the next
The watt-hour is a measure of capacity, or how much electrical energy a battery stores. If you know how much power — measured in watts —
Get Price
How many watts does it take to run a house?
In this article, we break down the typical energy use of different electrical appliances to help you determine the number of watts your whole house might require.
Get Price
How many watts does it take to run a house?
In this article, we break down the typical energy use of different electrical appliances to help you determine the number of watts your whole
Get Price
How Many Solar Watts Do You Need for Your Home?
People ask how many watts of solar do I need to match their energy use with the capacity of a solar system that can produce enough power all
Get Price
How Many Watts Do You Need To Power A House?
They usually operate within the range of 500-5,000 watts, depending on the size of the house and the type of heating method used. Cooling systems, such as air conditioners, also have varying
Get Price
Calculating Home Backup Battery Size: Load Estimation Tips
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know, from average household wattage to how you can calculate your home''s energy use
Get Price
How Many Batteries to Power a House? Backup and Off-Grid
Discover how many batteries to power a house for backup and off-grid solutions. Learn about energy needs, battery types, and cost-effective setups.
Get Price
How Many Watts Does It Take To Run Your House?
Here are the primary factors that determine how many watts you''ll need to run your house: The square footage of a home significantly impacts electricity consumption. The more rooms your
Get Price
How to Calculate Backup Power Needs for Your Home – Hinen
In summary, this household requires 12.24kWh of backup power to endure a 24-hour power outage. Three units of Hinen''s Max 5b 5kWh battery, or Base 5b (with 3 modules),
Get Price
Calculating Home Backup Battery Size: Load Estimation Tips
For example, if your critical loads require 2,000 watts of power and you need backup power for 24 hours, your total load would be 48,000 watt-hours (2,000 watts x 24
Get Price
How Many Watts to Power a House? A Practical
How Many Watts to Power a House: Calculating Your Energy Needs 1. Understanding Watts, Kilowatts, and Energy Consumption Before
Get Price
Backup Power Calculator
The Backup Power Calculator estimates and analyzes your backup power and energy needs. We do the math to help you determine how much solar and energy storage will be "enough" for you.
Get Price
How Long Can a Tesla Powerwall Power a House
Find out how long a Powerwall battery lasts and how many Powerwalls you need to power your home. Get a free quote for Tesla
Get Price
How Many Watts Are Needed To Run A House? –
To determine the number of watts your house is using, you''ll need to know two things: the number of watts it takes to power your appliances,
Get Price
How Many Watts Are Needed To Run A House? – Forbes Home
To determine the number of watts your house is using, you''ll need to know two things: the number of watts it takes to power your appliances, called running watts, and the
Get Price
Complete Guide to Home Battery Backup Systems
A house battery backup system is an energy storage solution that powers your home when the primary electrical grid fails. It stores electricity for later use, supplying power to
Get Price
Tesla Powerwall: how much of my house can I run on it
Continuous power is the power your battery can provide over a long period of time: for example, the power needed to keep your car running after it has been started. This will tell
Get Price
How Many Watts Does It Take To Run Your House?
Here are the primary factors that determine how many watts you''ll need to run your house: The square footage of a home significantly impacts electricity
Get Price
What Size Generator Do I Need? (With Easy To Use
However, there are two power output figures you need to be aware of when buying a generator: Continuous power rating (running watts) –
Get Price
Watts Required to Power a House: The Answer Revealed
Discover exactly how many watts your home needs to operate efficiently. This comprehensive guide breaks down power requirements by appliance, home size, and energy
Get Price
6 FAQs about [How many watts of energy storage power for the whole house]
How much wattage does a home need?
Notably, the wattage requirement of your home is highly dependent on the time of day and where you live; your power needs could be as high as several thousand watts at a certain point, and as low as a few hundred watts at another.
How much power does a house need?
Electrical equipment, such as televisions, computers, and gaming consoles, also contribute to a house’s power needs. Televisions can range from 50 watts for smaller models to over 300 watts for large, high-definition screens. Computers and gaming consoles usually require around 100-500 watts, depending on their specifications.
How much power does a battery system need?
For example, if your critical loads require 2,000 watts of power and you need backup power for 24 hours, your total load would be 48,000 watt-hours (2,000 watts x 24 hours). Once you have determined your total load, you can select a battery system that can meet your power needs.
How many Watts Does a home use a year?
The best way to save on electricity is to go solar – register on the EnergySage Marketplace today to compare your solar options. How many watts does an average home use? According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average American home uses an average of 10,791 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year.
How much power does a heating system use?
Heating systems, such as furnaces or electric heaters, can consume a significant amount of power. They usually operate within the range of 500-5,000 watts, depending on the size of the house and the type of heating method used. Cooling systems, such as air conditioners, also have varying wattage needs, typically ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 watts.
How many Watts Does a household use a day?
If you divide 10,715 kWh by 365 (days in a year), you’ll get the average number of kilowatt-hours used per day, which is 29.36 kWh. If you multiply that by 1,000, you can find the energy consumption in watts that occur in 24 hours, or 29,360 watts. If you then divide that by 24, you’ll find that the average household requires 1,223 watts of power.
More related information
-
 How much does Tanzanian energy storage power supply cost
How much does Tanzanian energy storage power supply cost
-
 How Many Volts of Energy Storage Power Supply Are Used in Substations
How Many Volts of Energy Storage Power Supply Are Used in Substations
-
 How many hybrid energy storage power stations are there in the United States
How many hybrid energy storage power stations are there in the United States
-
 How much does energy storage power cost in Cameroon
How much does energy storage power cost in Cameroon
-
 How many watts of solar power does the whole house generate
How many watts of solar power does the whole house generate
-
 How much does a solar energy storage power station cost
How much does a solar energy storage power station cost
-
 How many mobile energy storage sites and wind power does Albania control
How many mobile energy storage sites and wind power does Albania control
-
 How much is the price of lithium energy storage power supply in Malawi
How much is the price of lithium energy storage power supply in Malawi
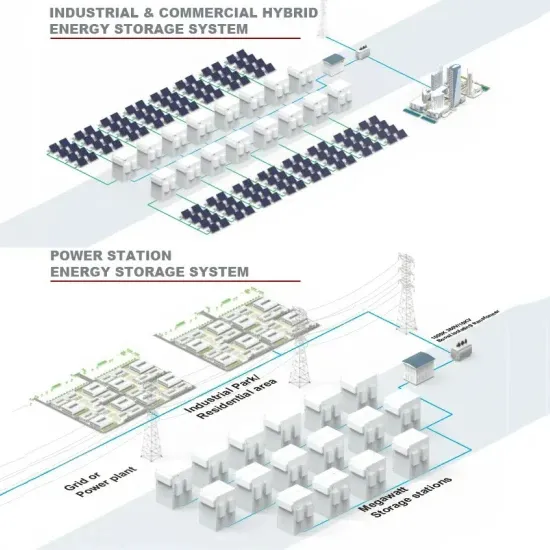
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


