Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
5G operates on everything from low-band frequencies below 1 GHz for broader coverage, up to mid-band between 1–6 GHz for faster speeds, and further on to high-band at millimeter-wave
Get Price
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously compared to previous generations of
Get Price
5G NR gNodeB base Stations
Featuring the latest in Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology to create gNodeB 5G Base Station functions, the 5G Baseband connects to Remote
Get Price
5G NR Base Station types
As per 3GPP specifications for 5G NR, it defines three classes for 5G NR base stations: These classes are as per cell types deployments like Macrocell, Microcell, and Pico cell. Wide Area
Get Price
Architecting a Software-Defined Base Station-on-a
EdgeQ Inc, a leader in 5G wireless infrastructure, today announced sampling of its revolutionary 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip to Tier 1
Get Price
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile Connectivity
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless mobile connectivity. These
Get Price
5G NR gNodeB base Stations
Featuring the latest in Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology to create gNodeB 5G Base Station functions, the 5G Baseband connects to Remote Radio Heads (RRH) via CPRI fibre
Get Price
Which RF Technologies Are Shaping 5G Base Stations?
5G base stations are the backbone of the 5G network, transmitting and receiving radio signals across various frequency bands to provide connectivity to mobile devices.
Get Price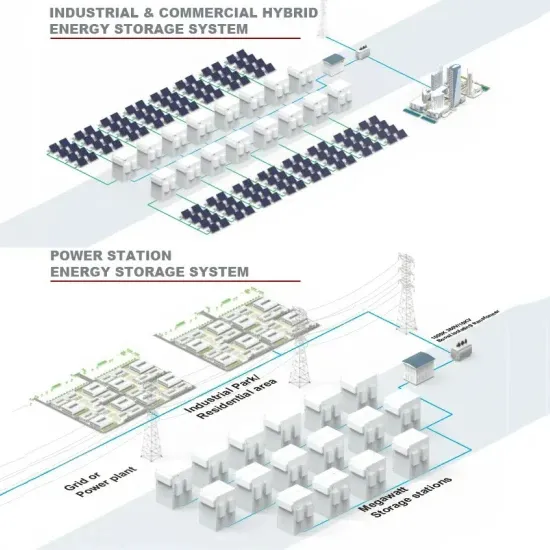
base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. It plays a central role in enabling wireless communication between user
Get Price
The Role of FPGA in 5G Technology and Beyond
Companies like Ericsson and Nokia have incorporated FPGA-based baseband processing units in their 5G base stations to efficiently
Get Price
What Is Radio Access Network (RAN) in 5G?
Ultra Dense Networks (UDN): 5G uses a denser base station layout than 4G. The large deployment of small base stations can improve coverage and capacity,
Get Price
Quick guide: components for 5G base stations and antennas
Base stations A 5G network base-station connects other wireless devices to a central hub. A look at 5G base-station architecture includes various equipment, such as a 5G
Get Price
Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base
5G base station chips must be compatible with 4G, 5G, and future 6G networks, supporting multi-band and technology standard switching to ensure seamless connection
Get Price
Collaborative optimization of distribution network and 5G base stations
In this paper, a distributed collaborative optimization approach is proposed for power distribution and communication networks with 5G base stations. Firstly, the model of 5G
Get Price
What is the main purpose of the Baseband unit (BBU) in Ericsson''s 5G
The Baseband Unit (BBU) in Ericsson''s 5G hardware plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of a 5G network. The BBU is responsible for processing and managing the
Get Price
base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. It plays a central role in enabling
Get Price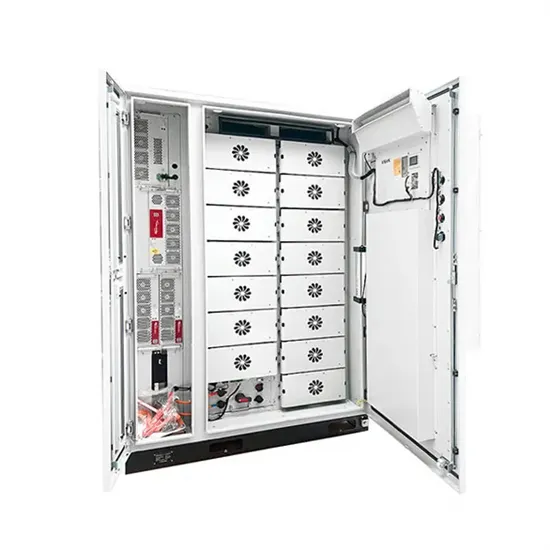
What Is A Base Station?
A base station is an integral component of wireless communication networks, serving as a central point that manages the transmission and
Get Price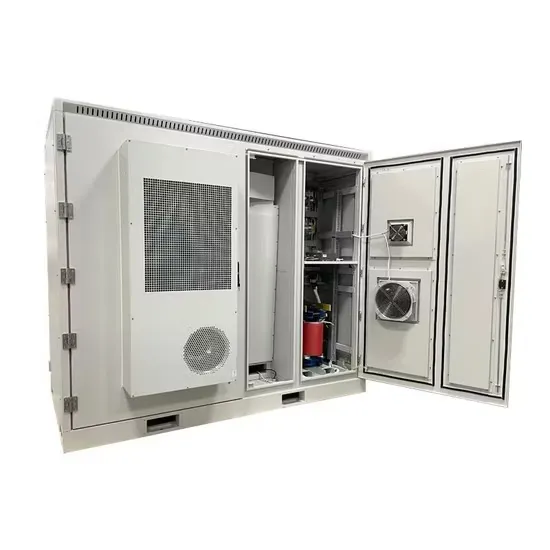
Optimize Signal Quality In 5G Private Network Base Stations
Optimize Signal Quality In 5G Private Network Base Stations With the rapid evolution of cellular communication systems, there is a growing need for higher operating frequencies and wider
Get Price
The challenges of building a 5G base station
Figure 1 shows the basic functional components required to build an integrated gNodeB base station. Figure 1. An integrated gNodeB includes
Get Price
What Is A 5G Base Station?
According to logical functions, 5G base stations can be divided into 5G baseband units and 5G radio frequency units, and the two can be connected through
Get Price
The challenges of building a 5G base station
Figure 1 shows the basic functional components required to build an integrated gNodeB base station. Figure 1. An integrated gNodeB includes a 5G Core, PHY, DFE and RF
Get Price
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture — 5G Mobile Networks:
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture ¶ This chapter identifies the main architectural components of cellular access networks. It focuses on the components that
Get Price
5G Technology and Transceiver Architecture
5G deployment use cases can be categorized into three broad areas: enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive
Get Price
An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize
This article described the basics of 5G and introduced two MPS parts — the MPQ8645 and MP87190 — that can be used to improve the AAU or BBU architecture within a 5G base cell
Get Price
Accelerating 5G Baseband With Adaptive SoCs
In the next post, we''ll dive into some specifics about Telco Accelerator Cards, while also touching on what''s next for 5G baseband acceleration. Related Accelerating 5G
Get Price
Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
5G base station chips must be compatible with 4G, 5G, and future 6G networks, supporting multi-band and technology standard switching to ensure seamless connection
Get Price
What Is A 5G Base Station?
According to logical functions, 5G base stations can be divided into 5G baseband units and 5G radio frequency units, and the two can be connected through CPRI or eCPRI interfaces.
Get Price
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Which 5G baseband is suitable for 5G communication base stations ]
What are the different types of 5G NR base stations?
This article describes the different classes or types of 5G NR Base Stations (BS), including BS Type 1-C, BS Type 1-H, BS Type 1-O, and BS Type 2-O. 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB.
Are 5G base station chips compatible with 4G & 6G networks?
5G base station chips must be compatible with 4G, 5G, and future 6G networks, supporting multi-band and technology standard switching to ensure seamless connection between generations of networks.
What is a 5G baseband unit?
The 5G baseband unit is responsible for NR baseband protocol processing, including the entire user plane (UP) and control plane (CP) protocol processing functions, and provides a backhaul interface (NG interface) with the core network and an interconnection interface (Xn interface) between base stations ).
How does a 5G base station work?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously compared to previous generations of mobile networks. They are designed to handle the increased data traffic and provide higher speeds by operating in higher frequency bands, such as the millimeter-wave spectrum.
Why are 5G base station chips important?
As 5G technology matures and manufacturing processes are optimized, the cost of base station chips will gradually decrease, thereby promoting the wider deployment of 5G networks. 5G base station chips play a critical role in the construction of 5G networks.
How does the architecture of a base station affect 5G?
The architecture and shape of the base station directly affect how the 5G network is deployed. In the technical standards, the frequency band of 5G is much higher than that of 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
More related information
-
 Which UAE communication company has more 5G base stations
Which UAE communication company has more 5G base stations
-
 Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
-
 Which is the most popular inverter for communication base stations in Afghanistan
Which is the most popular inverter for communication base stations in Afghanistan
-
 Germany has 5G base stations for communication
Germany has 5G base stations for communication
-
 Which is the best power module supplier for communication base stations in Cambodia
Which is the best power module supplier for communication base stations in Cambodia
-
 Albania s first batch of 5G communication base stations
Albania s first batch of 5G communication base stations
-
 Is it suitable to build a 5G communication base station on the roof
Is it suitable to build a 5G communication base station on the roof
-
 How to check 5G base stations in communication
How to check 5G base stations in communication
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


