What is a 5G Base Station?
These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises. A 5G base station is a critical
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get Price
5g base station architecture
5G (fifth generation) base station architecture is designed to provide high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity to a wide range of devices. The architecture is more
Get Price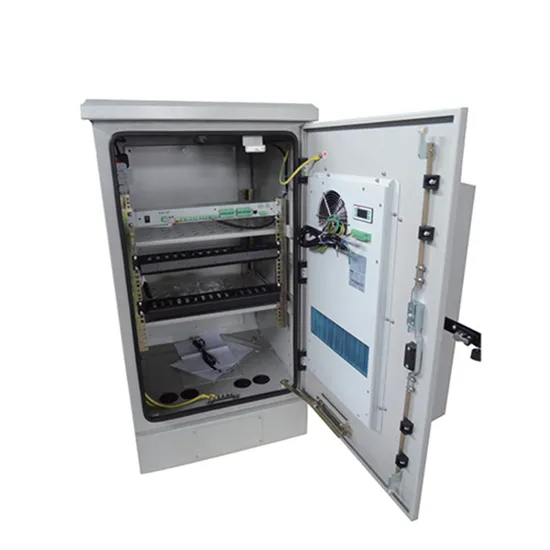
What is a 5G Base Station?
These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises. A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network
Get Price
Review on 5G small cell base station antennas: Design
Small-cell Base Station (SBS) antennas are crucial for exploring the full potential of 5G networks by expanding the network in urban areas, densely populated regions, indoor environments,
Get Price
The 5G Base Stations: All Technologies On Board
In addition to the immense challenges of operating there, this leap will require every viable semiconductor technology to generate RF power for the transmit
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless
Get Price
Location of 5G base station antenna in substation taking into
1. Considering the influence of 5G high-frequency electromagnetic wave on the electrical equipment in the substation, the positioning accuracy of 5G base station antenna in
Get Price
Small Cell Networks: Overview of High-Level
Table 1: Small Cell Deployment Scenarios High-Level Architecture: The high-level architecture of a 5G small cell typically includes
Get Price
Types of 5G NR Base Stations: A Comprehensive Overview
Each type of base station serves a specific purpose, from broad coverage with macro cells to ultra-fast speeds with mmWave technology. Understanding these base stations helps network
Get Price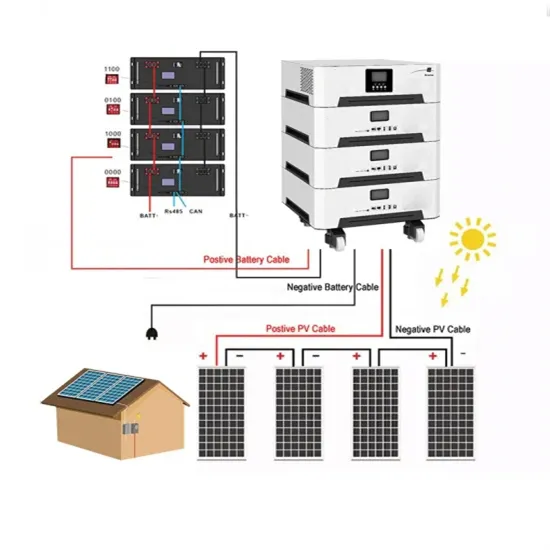
Optimization of 5G base station deployment based on quantum
In previous research on 5 G wireless networks, the optimization of base station deployment primarily relied on human expertise, simulation software, and algorithmic optimization. The
Get Price
What Is 5G Base Station?
With the advent of the 5G era, in order to ensure stable signal transmission and wider coverage, the construction of 5G base stations as the "pioneers" of 5G large-scale
Get Price
The 5G Base Stations: All Technologies On Board
In addition to the immense challenges of operating there, this leap will require every viable semiconductor technology to generate RF power for the transmit sections of base stations of
Get Price
What Is A Base Station?
A base station is an integral component of wireless communication networks, serving as a central point that manages the transmission and
Get Price
5G Basics: Everything You Need to Know
The 5G network primarily consists of three main components: UE (User Equipment: terminal devices), gNB (gNodeB: base stations, gNB is
Get Price
Macrocell vs. Small Cell vs. Femtocell: A 5G introduction
5G networks also use macrocells, such as cell towers, for connectivity. These larger base stations enable lower 5G frequencies, compared to small cells'' high-frequency
Get Price
5g base station architecture
5G base stations often use Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology and beamforming to enhance spectral efficiency and coverage. Massive MIMO
Get Price
What is 5G base station architecture?
Before you can think about 5G network components, you need to consider the base station. To get started, find out what you need to know about the architecture.
Get Price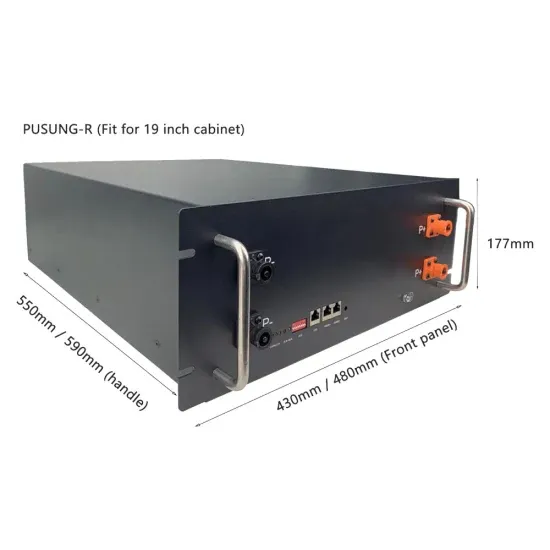
The Applicability of Macro and Micro Base Stations for 5G Base Station
This paper concludes that in the case of large-scale coverage of macro base stations, micro base stations supplement signal blind spots. Finally, the work gives forward
Get Price
The business model of 5G base station energy storage
In terms of 5G base station energy storage system, the literature [1] constructed a new digital ''mesh'' power train using high switching speed power semiconductors to transform the
Get Price
5G Network Equipment Manufacturers: Modem, Base Station,
5G RAN The 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) is the interface between user devices and the 5G core network. It comprises base stations and small cells that manage radio communications,
Get Price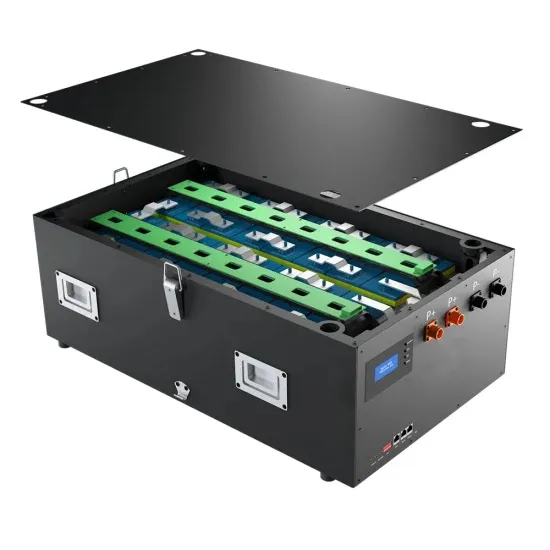
What is 5G base station architecture?
Before you can think about 5G network components, you need to consider the base station. To get started, find out what you need to know
Get Price
What Are Base Stations in 5g? – Smart Solar
3 function: base station equipment can be divided into baseband unit (BBU) and radio frequency unit (AAU/RRU), where the BBU is responsible for handling signaling and data from
Get Price
Guide to Small Cells, HetNets and 5G
The number of 5G or multimode small cell deployments is expected to top a million in 2020 and grow strongly thereafter, reaching 5.2 million (62%) of total deployments in 2025.
Get Price
A guide to 5G small cells and macrocells
Small-cell base stations, known as transceivers, use low power and are implemented in densely populated areas and are cheaper and much
Get Price
What is 5g base station architecture
It facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and the core network. The architecture of a 5G base station is designed to support higher data rates, lower
Get Price
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The Key to
Base station, also known as BTS (Base Transceiver Station), is a key device in wireless communication systems such as GSM. Equipped with an electromagnetic wave
Get Price
Investigating the Sustainability of the 5G Base Station
5G is the next generation of wireless communication tech-nology that will significantly improve network bandwidth and decrease latency. There are two key wireless communication
Get Price
What Is 5G Base Station?
With the advent of the 5G era, in order to ensure stable signal transmission and wider coverage, the construction of 5G base stations as the
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Are 5G communication base stations divided into large and small sizes ]
What are the components of a 5G base station?
Key Components of A 5G Base Station: Antennas and Radios: The Base Station Includes Antennas and Radio Units Responsible for Transmitting and Receiving Signals. Multiple antennas may be used for MOMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), Enhancing Coverage, Capacity, and Overall Network Efficiency.
What is 5G base station architecture?
5G base station architecture is characterized by its flexibility, virtualization, and the ability to support diverse services through network slicing. The separation of CU and DU, along with the introduction of cloud-based technologies, allows for more efficient resource utilization and scalability.
Why do 5G base stations use MIMO & beamforming?
Both are critical for ensuring seamless communication between different network elements. 5G base stations often use Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology and beamforming to enhance spectral efficiency and coverage. Massive MIMO involves using a large number of antennas to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously.
What are the components of a 5G core network?
The key components of a 5G core network are seen here: User Equipment (UE): 5G cellular devices, such as smartphones, connect via the 5G New Radio Access Network to the 5G core and then to the internet. Radio Access Network (RAN): Coordinate network resources across wireless devices.
What are base stations in 4G LTE networks called?
The base stations in 4G LTE networks are called either evolved Node B or eNodeB. You’ll find that eNodeB is usually abbreviated as eNB in 5G network architecture diagrams, and gNodeB as gNB. It helps to keep mind that a base station called eNB is for 4G, and gNB is for 5G.
Can small cells connect to 5G networks?
Small cells provide fast connectivity speeds for 5G networks and capable devices, but 5G won't stop there. Macrocells and femtocells are also key to connect 5G networks. Small cell technology has been touted as a major development with 5G networks, but small cells aren't the only base stations that provide 5G connectivity.
More related information
-
 Germany has 5G base stations for communication
Germany has 5G base stations for communication
-
 Which 5G baseband is suitable for 5G communication base stations
Which 5G baseband is suitable for 5G communication base stations
-
 Can photovoltaic communication 5g base stations be used
Can photovoltaic communication 5g base stations be used
-
 Which UAE communication company has more 5G base stations
Which UAE communication company has more 5G base stations
-
 Communication 5G base stations are too concentrated
Communication 5G base stations are too concentrated
-
 Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
-
 Does 5G communication use shared base stations
Does 5G communication use shared base stations
-
 How many base stations are there for 5G communication
How many base stations are there for 5G communication
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


